In trading companies and manufacturing companies, there are two reports that must be made, namely the cost of goods manufactured report and the cost of goods sold report.
As we all know that the cost of goods sold must be calculated correctly because it will determine the selling price according to the consumer or according to the market.
So, how do you calculate the cost of goods sold report? What formula can be used? Find the answer by reading this article to the end.
Contents
1 Definition of Cost of Goods Sold
2 Benefits of Cost of Goods Sold
3 Methods of Cost of Goods Sold
3.1 1. FIFO (First In First Out) Method
3.2 2. LIFO (Last In First Out) Method
3.3 3. Average Method (Average Method)
4 Various Factors Affecting Cost of Goods Sold
4.1 1. Production Cost
4.2 2. Beginning Stock
4.3 3. Ending inventory
4.4 4. Net Purchase
4.5 5. Purchase Freight Cost
4.6 6. Purchase Returns
4.7 7. Purchase Discount
5 Ways to Calculate and Make a Cost of Goods Sold Report for a Trading Company
6 Cost of Goods Sold Report
6.1 Case Example of Cost of Goods Sold Report 1
6.2 Sample Sales Price Report Case 2
Definition of Cost of Goods Sold
As we all know that the cost of goods sold or HPP are all costs incurred by the company, either directly or indirectly, to obtain goods sold or the price obtained from goods or services to be sold.
The cost of goods sold cannot be equated with the selling price, the selling price is the price charged to consumers or to buyers of goods. The value in this selling price must be greater than the cost of goods sold so that the company continues to make a profit.
By calculating the sales price correctly, it will be easier to determine the appropriate selling price for customers.
Cost of Goods Sold Benefits
The benefit of calculating the cost of goods sold is to be able to determine the cost of production and selling price, as well as to know the value of the profit that the company wants to get.
When the selling price is greater than the cost of goods sold, the company can make a profit. On the other hand, if the selling price is lower than the cost of goods sold, the company will lose.
Cost of Goods Sold Method
There are three methods in calculating the cost of goods sold report, namely the FIFO method, the LIFO method, and the average method. Here is the explanation.
1. FIFO Full Form (First In First Out) Method
This method will assume that the cost of goods sold must be charged to profit in the order in which the goods were purchased. The goods that are purchased for the first time must be sold first and vice versa.
This method will be able to get a lot of gross profit when market price conditions continue to increase or inflation. So, the cost of goods sold first will be lower than the cost of goods purchased last.
If inflation occurs, the company will later earn a smaller gross profit, because prices in the market continue to decline.
2. LIFO Full Form (Last In First Out) Method
The opposite of the FIFO method, the LIFO method is calculated using the price of the goods that entered the warehouse last and will go out first.
Goods that have not been sold and whose inventory is still there are goods that enter the warehouse in the initial period of purchase.
The calculation of the cost of goods is based on the stocktaking at the end of the period. This method will get a larger cost of goods sold and a smaller gross profit because it has a smaller amount of inventory at the end of the period. But if there is inflation, then the amount of gross profit that will be obtained will be more.
3. Average Method ( Average Method )
This method has a correlation that is in line with price fluctuations and is between the LIFO and FIFO methods. The calculation of the cost of goods sold will be based on existing stock and the same average price within a certain period of time. Here is the explanation
1. The simple average method or simple average method is calculated by dividing purchases by the number of items purchased at the end of the period.
2. Moving average method or weighted average method that calculates the price at the time of purchase multiplied by the goods purchased, then proceed by dividing the number of goods purchased at the end of the period.
3. The moving average method or the moving average method is the average price purchased for each purchase.
Various Factors Affecting Cost of Goods Sold
1. Production Cost
These production costs include direct labor costs, overhead costs and raw material costs. The cost of raw materials is the cost of the initial inventory of raw materials added to the cost of purchasing raw materials and then deducted by the cost of the ending inventory of raw materials.
Meanwhile, direct labor costs are costs that are charged to employees whose services are used directly. Meanwhile, overhead costs are all production costs that do not include raw material costs and also direct labor costs, such as indirect labor, electricity costs, internet, and various other costs.
2. Beginning Stock
Beginning inventory costs are costs that are still in stock prior to the manufacturing process. These costs can be found in the company’s beginning balance sheet in the previous year, or it can also be found in the current period’s trial balance.
3. Ending Supplies
The cost of ending inventory is a cost that is calculated based on the remaining production materials or inventory remaining at the end of the period. This cost is calculated so that later there will be nothing wrong in the production process and it is hoped that there will be material left to be used again.
You can find the ending inventory balance in the ending balance in the company’s financial statements.
4. Net Purchase
Net purchases are the total number of purchases of merchandise, either in cash or on credit, plus the transportation costs of purchases and minus purchase discounts and purchase returns.
5. Purchase Freight Cost
This fee is the cost of shipping the goods borne by the buyer. Later, the goods must be sent directly from the seller’s warehouse to the buyer of the goods.
6. Purchase Returns
Purchase returns are the costs of returning goods due to defects or damage when the goods are received. However, purchases of goods made on credit when there is a purchase return can be reduced by accounts payable.
7. Purchase Discount
A purchase discount is a reduction in price or value when a customer purchases an item.
How to Calculate and Make a Cost of Goods Sold Report for a Trading Company
Generally, trading companies will only buy goods that are ready to be resold. So there will only be one inventory account, namely the inventory account. Thus, the inventory of goods and the determination of the cost of goods sold will be closely related to one another.
The following is the calculation formula.
- Net sales = sales of goods – (sales returns + sales discounts)
- Net purchases = (purchases + purchase freight) – (purchase returns + purchase discounts)
- Inventory of goods = beginning inventory of goods + net purchases
- Cost of goods sold = beginning inventory of goods – ending inventory of goods
Examples of Cost of Goods Sold (COGS)
XYZ Ltd. has the following inventory accounting information for the calendar year ended December 31, 2018.
Inventories at the beginning of the January 1, 2018 calendar year are $11,000 and the inventories at the end of the December 31, 2018 calendar year are $3,000. During the calendar year, the company makes purchases of $6,000. Calculate the cost of goods sold for the calendar year ending December 31, 2018.
Solution
Using the above details, the COGS(Cost of Goods Sold) will be calculated for the year ending on December 31st, 2018, for company XYZ Ltd.
Calculation of Cost of Goods Sold is as follows –
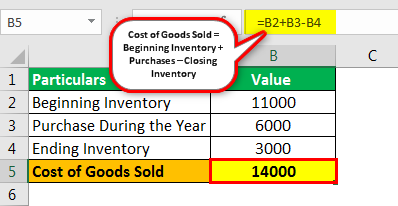
Cost of Goods Sold formula = Beginning Inventory + Purchases – Ending Inventory.
Cost of Goods Sold = $11,000 + $6,000 – $3,000
Cost of Goods Sold = $14,000
Analysis
Thus, in this case, the value of goods sold by XYZ Ltd. is $14,000 for the year ended December 31, 2018. This figure is important for the company as it will help it make better decisions. For example, suppose the same material is available in the market at a better price. Here the company will compare the prices and make a choice in favor of low cost with equal quality of the products.
Along with estimating costs and profits, cost of goods sold will also help the business plan its purchasing for the coming year, as the business will know what is in opening stock and what is left over as final inventory. buy in subsequent years.